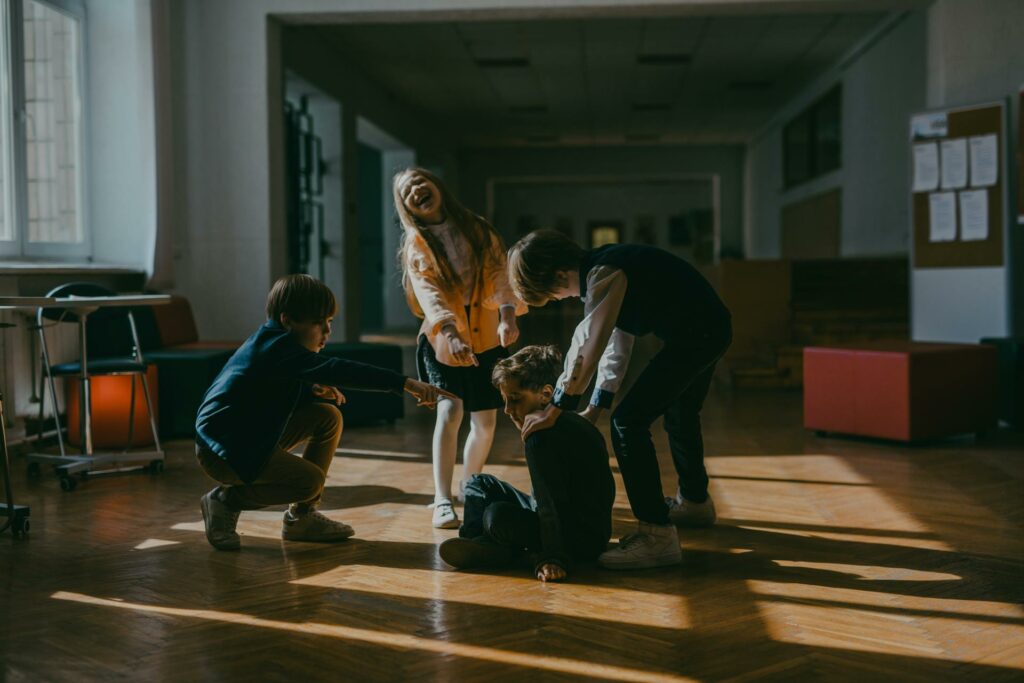
Bullying in schools is a widespread issue, affecting students’ emotional, social, and academic well-being. Understanding the various types of bullying and implementing effective strategies to prevent and address them is crucial for fostering a safe and inclusive school environment.
This blog explores the types of bullying that occur in schools, offers actionable solutions, and addresses frequently asked questions to help educators and parents combat this issue effectively.
What is Bullying?
Bullying is intentional, repeated, and harmful behaviour designed to intimidate, humiliate, or hurt another person. It can occur in various forms, each with unique characteristics and challenges.
The Types of Bullying in Schools
- Physical Bullying
This involves physical harm or aggression, such as hitting, pushing, or damaging property. It is often the most visible form of bullying. - Verbal Bullying
Verbal bullying includes name-calling, teasing, threats, and derogatory remarks. It can significantly affect a child’s self-esteem and emotional health. - Social (Relational) Bullying
Social bullying in schools occurs when someone’s reputation or relationships are deliberately damaged. Examples include spreading rumours, excluding someone from a group, or public humiliation. - Cyberbullying
This form of bullying takes place online through social media, messaging apps, or gaming platforms. Cyberbullying can be particularly damaging due to its pervasive and often anonymous nature. - Prejudicial Bullying
Prejudicial bullying is based on biases related to race, religion, gender, or other personal characteristics. This type of bullying often stems from stereotypes and can escalate to serious discrimination. - Sexual Bullying
Sexual bullying includes inappropriate comments, gestures, or actions of a sexual nature. This type of bullying can significantly impact a student’s sense of safety and dignity.
Combating Bullying: Preventive Measures and Interventions
- Foster Awareness and Education
Schools should educate students, teachers, and parents about the types of bullying and their impact. Regular workshops, assemblies, and anti-bullying campaigns can create awareness. - Encourage Open Communication
Create a safe environment where students feel comfortable reporting bullying. Encourage open conversations between students, teachers, and parents to address concerns early. - Establish Clear Policies
Schools should implement anti-bullying policies outlining the definition of bullying, reporting procedures, and consequences for offenders. Ensure these policies are consistently enforced. - Promote Empathy and Respect
Incorporate social-emotional learning (SEL) into the curriculum to teach students empathy, conflict resolution, and the value of diversity. - Monitor and Supervise
Increase adult supervision in bullying hotspots such as playgrounds, cafeterias, and hallways. Prompt intervention can deter bullying behaviour. - Utilize Technology Wisely
Educate students about responsible online behaviour and the risks of cyberbullying. Schools can also monitor digital platforms used for learning to ensure safe interactions. - Support the Victims
Provide counselling and support to victims of bullying to help them rebuild confidence and address emotional distress. - Address Bullying Behaviour
Work with bullies to understand the root causes of their behaviour and provide guidance or therapy to promote positive change.
Examples of School Bullying
- A student being teased relentlessly for their appearance (verbal bullying).
- Spreading false rumours about a peer to damage their reputation (social bullying).
- A group of students repeatedly excluding a classmate from activities (social bullying).
- Sending threatening messages through a social media platform (cyberbullying).
- Pushing or tripping a student in the hallway (physical bullying).
Understanding the Causes of Bullying in Schools
Bullying behaviour can stem from various factors, including:
- Power Imbalance
Bullies often target individuals they perceive as weaker or less confident. - Lack of Empathy
Children who struggle with understanding others’ emotions may resort to bullying. - Environmental Influence
Negative family dynamics, exposure to aggression at home, or a lack of discipline can contribute to bullying tendencies. - Peer Pressure
Students may engage in bullying to gain acceptance or status within a peer group. - Unsupervised Settings
Areas with minimal adult supervision often become hotspots for bullying behaviour.
Conclusion
Bullying in schools is a serious issue that requires a collective effort to combat. By understanding the various types of bullying and implementing preventive measures, schools and parents can create a safe, supportive environment where all students can thrive.
For more resources and support in addressing bullying and promoting a positive school culture, visit Open Minds Campus.
Answering Common Questions
What are the types of bullying at school?
Physical, verbal, social, cyber, prejudicial, and sexual bullying are the main types observed in schools.
What are three types of bullying?
The three common types of bullying are physical, verbal, and social bullying.
What are examples of school bullying?
Examples include teasing someone about their appearance, spreading rumours, physical aggression, or cyberbullying through hurtful online messages.
What are the causes of bullying in schools?
Bullying can arise from power imbalances, lack of empathy, environmental influences, peer pressure, or unsupervised environments.